Exploring the Applications of PLC Controllers and Modules in Automation
Jun 05, 2024
Title: Exploring the Applications of PLC Controllers and Modules in Automation
Introduction:PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems play a crucial role in modern automation processes. These robust controllers, integrated with various modules, enable precise control over industrial machinery and processes. Let's delve into the diverse applications where PLC controllers and modules find extensive use.
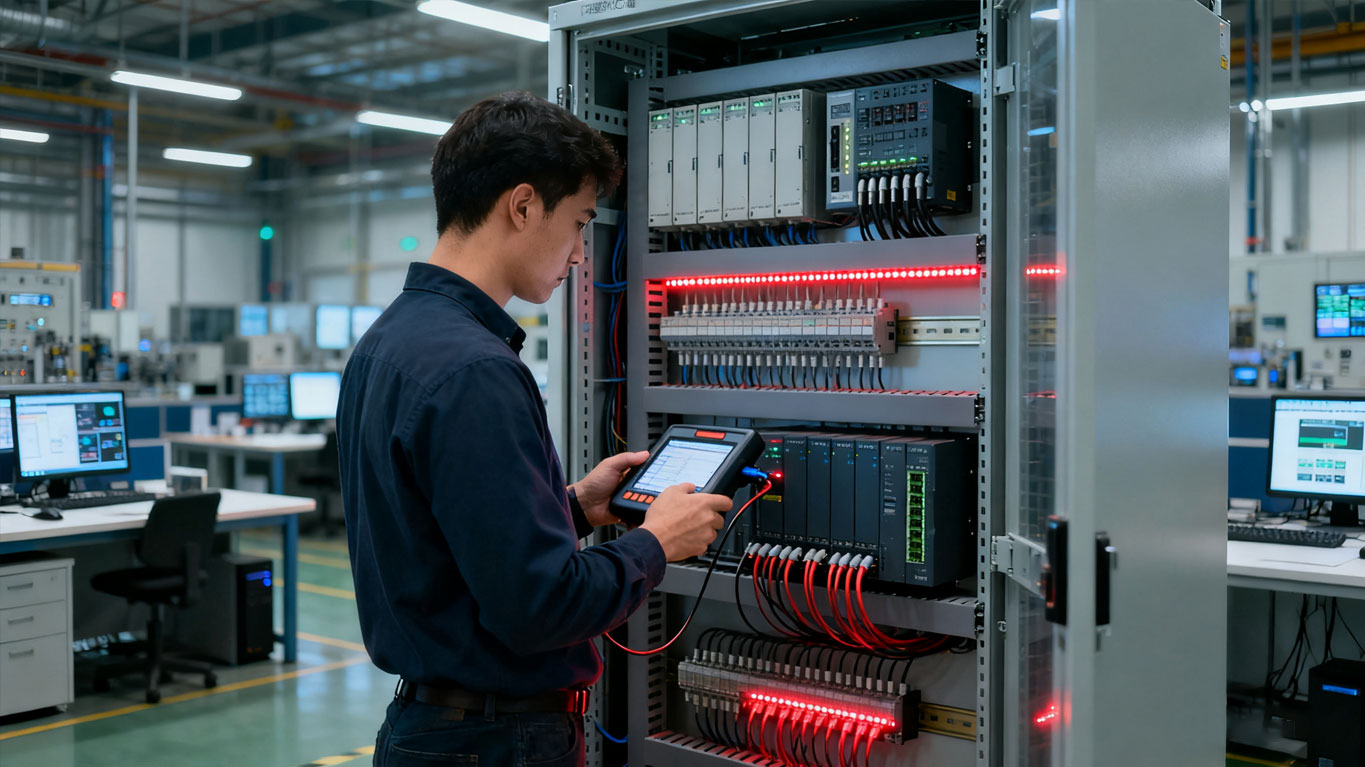
Manufacturing Industry:PLC controllers and modules drive efficiency and scalability in the manufacturing sector. They facilitate seamless coordination of production lines, ensuring synchronized operation among different machines and optimizing productivity. With their flexible programming capabilities, PLCs can adapt to changing manufacturing requirements swiftly.
Building Automation:PLC controllers have revolutionized building automation systems, empowering facilities to optimize energy consumption, enhance security, and streamline operations. Various modules can monitor and control HVAC, lighting, access control, fire alarms, and more, enabling intelligent management of building infrastructure.
Process Control:In industries like oil refining, chemical production, and wastewater treatment, PLC controllers coupled with specialized modules excel in process automation and control. They regulate variables such as temperature, pressure, flow rates, and chemical dosing, ensuring consistent quality, safety, and adherence to stringent regulations.
Transportation Systems:PLC controllers and modules are integral to modern transportation systems, controlling operations in railways, airports, and traffic management. From signaling and train dispatching to baggage handling and passenger information displays, PLCs provide real-time monitoring and coordination, ensuring efficient and safe transportation.
Renewable Energy:PLC controllers enable intelligent management of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. By integrating with monitoring modules, they gather data on energy generation, consumption, and storage. This information allows operators to optimize energy distribution, maximize efficiency, and enhance grid stability.
Robotics and Motion Control:PLC controllers and motion control modules are at the heart of robotic operations, enabling precise movement coordination and control. From industrial robots on assembly lines to complex robotic arms in research applications, PLCs provide the necessary intelligence to execute complex tasks with accuracy and speed.
Conclusion:PLC controllers and modules have diverse applications across industries, facilitating automation, control, and monitoring of critical processes. These versatile components empower businesses to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, enhance safety, and adapt to evolving technological advancements. As automation continues to shape the future, the role of PLCs remains pivotal in driving innovation and realizing the potential of modern-day industries.